814-49-3
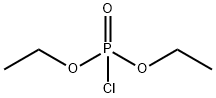
Product Name:
Diethyl chlorophosphate
Formula:
C4H10ClO3P
Synonyms:
Diethyl phosphorochloridate
Inquiry
CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Diethyl chlorophosphate is a clear liquid. This material is used as an intermediate in organic synthesis. (EPA, 1998) |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | Water-white liquid |
| Boiling Point | 140 °F at 2 mmHg (EPA, 1998) |
| Solubility | Sol in alcohols |
| Density | 1.1915 at 77 °F (EPA, 1998) - Denser than water; will sink |
| Vapor Density | 5.94 (EPA, 1998) - Heavier than air; will sink (Relative to Air) |
| Decomposition | When heated to decomposition it emits ... very toxic fumes of /hydrogen chloride and phosphorous oxides/. |
| Refractive Index | Index of refraction: 1.4153 @ 25 °C |
| Chemical Classes | Other Classes -> Organophosphates, Other |
SAFETY INFORMATION
| Signal word | Danger |
|---|---|
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H331:Acute toxicity,inhalation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P262:Do not get in eyes, on skin, or on clothing. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 172.55 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 172.0056089 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 172.0056089 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 35.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 9 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 106 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Diethyl chlorophosphate is a clear liquid. This material is used as an intermediate in organic synthesis. (EPA, 1998)
