7782-63-0
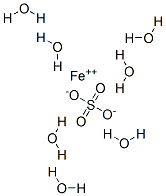
Product Name:
Ferrous sulfate heptahydrate
Formula:
FeH14O11S
Synonyms:
o-Phenanthroline ferrous sulfate complex;1,10-Phenanthroline iron(II) sulfate complex;Ferrous sulfate heptahydrate;Iron vitriol;Iron(II) sulfate heptahydrate
Inquiry
CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Pellets or Large Crystals |
|---|---|
| Chemical Classes | Metals -> Metals, Inorganic Compounds |
SAFETY INFORMATION
| Signal word | Warning |
|---|---|
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 278.02 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 11 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 277.960618 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 277.960618 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 95.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 13 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 62.2 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 9 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Iron(2+) sulfate heptahydrate is a hydrate that is the heptahydrate form of iron(2+) sulfate. It is used as a source of iron in the treatment of iron-deficiency anaemia (generally in liquid-dosage treatments; for solid-dosage treatments, the monohydrate is normally used). It has a role as a nutraceutical, an anti-anaemic agent and a reducing agent. It is a hydrate and an iron molecular entity. It contains an iron(2+) sulfate (anhydrous).
