CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| LogP | 5.39 |
|---|
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 492.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 5.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 492.24243570 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 492.24243570 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 77.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 36 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 821 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 7 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
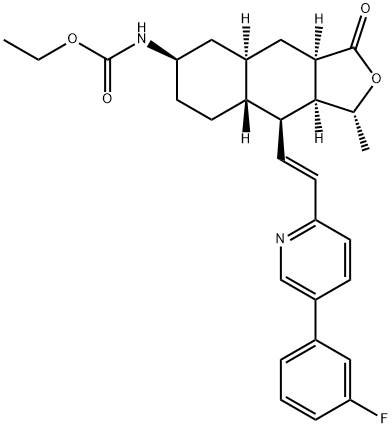
Vorapaxar is a carbamate ester that is the ethyl ester of [(1R,3aR,4aR,6R,8aR,9S,9aS)-9-{(E)-2-[5-(3-fluorophenyl)pyridin-2-yl]ethynyl}-1-methyl-3-oxododecahydronaphtho[2,3-c]furan-6-yl]carbamic acid. A protease-activated receptor-1 antagonist used (as its sulfate salt) for the reduction of thrombotic cardiovascular events in patients with a history of myocardial infarction (MI) or with peripheral arterial disease. It has been shown to reduce the rate of a combined endpoint of cardiovascular death, MI, stroke and urgent coronary revascularisation. It has a role as a protease-activated receptor-1 antagonist, a platelet aggregation inhibitor and a cardiovascular drug. It is a member of pyridines, a carbamate ester, an organofluorine compound, a naphthofuran and a lactone. It is a conjugate base of a vorapaxar(1+).