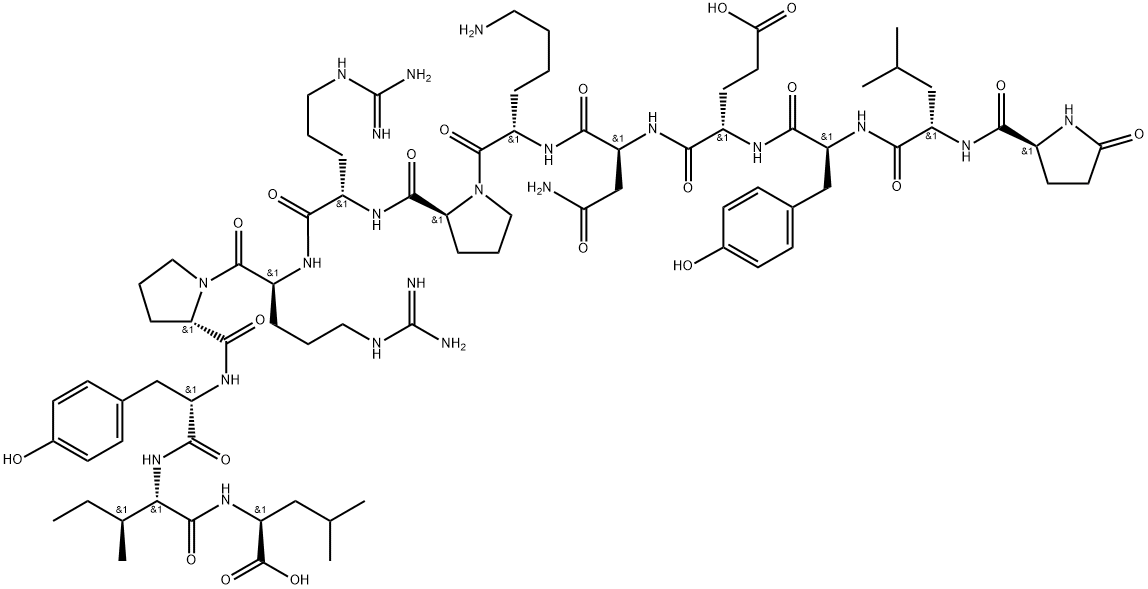
CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Collision Cross Section | 526.7 Ų [M+3H]3+ 434.9 Ų [M+2H]2+ |
|---|
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 1672.9 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | -3.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 21 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 23 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 50 |
| Exact Mass | 1671.90967533 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 1671.90967533 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 674 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 119 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 3530 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 14 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Neurotensin is a 13 amino acid peptide hormone which is found in the central nervous system and the gastrointestinal tract. It behaves as a neurotransmitter in the brain, as a hormone in the gut, and also as a neuromodulator. It is implicated in the pathophysiology of several CNS disorders (including schizophrenia, Parkinson's disease, drug abuse, pain, cancer, inflammation, eating disorders and central control of blood pressure) due to its association with a wide variety of neurotransmitter systems such as dopaminergic, sertonergic, glutamatergic, GABAergic, and cholinergic systems. It has a role as a human metabolite, a mitogen, a neurotransmitter and a vulnerary. It is a conjugate base of a neurotensin(1+).