CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Solid |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 398ºC (estimate) |
| Melting Point | 120 °C |
| Solubility | Soluble (tartrate form) |
| LogP | 2.15 |
| Caco2 Permeability | -4.59 |
| Dissociation Constants | 9.56 |
| Collision Cross Section | 172.7 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: TW, Method: Major Mix IMS/Tof Calibration Kit (Waters)] |
| Other Experimental Properties | White crystalline powder; freely soluble in water; soluble in methanol; sparingly soluble in ethanol; slightly soluble in dichloromethane and 2-propanol; practically insoluble in ethyl acetate, acetone, diethylether and heptane /Metoprolol succinate/ |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 267.36 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 1.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 9 |
| Exact Mass | 267.18344366 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 267.18344366 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 50.7 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 215 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
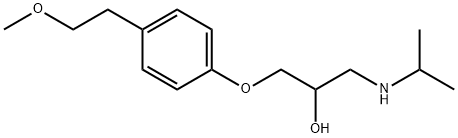
Metoprolol is a propanolamine that is 1-(propan-2-ylamino)propan-2-ol substituted by a 4-(2-methoxyethyl)phenoxy group at position 1. It has a role as a beta-adrenergic antagonist, an antihypertensive agent, a xenobiotic, an environmental contaminant and a geroprotector. It is a propanolamine, an aromatic ether, a secondary alcohol and a secondary amino compound.