CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Solid |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 160 °C at 1.00E-01 mm Hg |
| Melting Point | < 25 °C |
| Solubility | 2.28e-01 g/L |
| LogP | 2.6 |
| Kovats Retention Index | 2047 2109 2067 2060 2052 2065 2066.7 2063.3 2070 2075 2080 |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 290.79 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 2.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 290.1185909 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 290.1185909 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 25.4 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 20 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 267 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
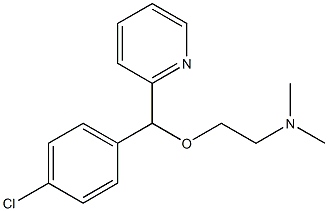
Carbinoxamine is an organochlorine compound that is 2-(4-chlorobenzyl)pyridine in which one of the benzylic hydrogens is substituted by 2-(dimethylamino)ethoxy group. It is an ethanolamine-type antihistamine, used as its maleate salt for treating hay fever, as well as mild cases of Parkinson's disease. It has a role as a H1-receptor antagonist, an anti-allergic agent, a muscarinic antagonist and an antiparkinson drug. It is a member of pyridines, a tertiary amino compound and a member of monochlorobenzenes.