CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Solid |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | Crystals from ethyl acetate |
| Melting Point | 228-229.5 °C |
| Solubility | Insoluble in water |
| LogP | log Kow = 2.12 |
| Stability/Shelf Life | Stable under recommended storage conditions. |
| Decomposition | When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of /hydrogen chloride/ and /nitric oxides/. |
| Collision Cross Section | 171.5 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: TW, Method: Major Mix IMS/Tof Calibration Kit (Waters)] |
| Kovats Retention Index | 2910 2910 2908 2936 2936 2910 2902.8 |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 308.8 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 2.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 308.0828741 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 308.0828741 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 43.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 434 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
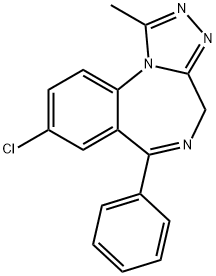
Alprazolam is a member of the class of triazolobenzodiazepines that is 4H-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a][1,4]benzodiazepine carrying methyl, phenyl and chloro substituents at positions 1, 6 and 8 respectively. Alprazolam is only found in individuals that have taken this drug. It has a role as an anxiolytic drug, an anticonvulsant, a muscle relaxant, a sedative, a GABA agonist and a xenobiotic. It is a triazolobenzodiazepine and an organochlorine compound.