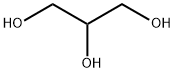
| Physical Description |
Glycerine appears as a colorless to brown colored liquid. Combustible but may require some effort to ignite. |
| Color/Form |
Syrupy, rhombic plates |
| Odor |
MILD ODOR |
| Taste |
Sweet, warm taste |
| Boiling Point |
554 °F at 760 mmHg (decomposes) (NTP, 1992) |
| Melting Point |
64 °F (NTP, 1992) |
| Flash Point |
320 °F (NTP, 1992) |
| Solubility |
greater than or equal to 100 mg/mL at 64 °F (NTP, 1992) |
| Density |
1.261 at 68 °F (USCG, 1999) - Denser than water; will sink |
| Vapor Density |
3.17 (NTP, 1992) - Heavier than air; will sink (Relative to Air) |
| Vapor Pressure |
0.0025 mmHg at 122 °F ; 40 mmHg at 388 °F (NTP, 1992) |
| LogP |
log Kow = -1.76 |
| Henry's Law Constant |
Henry's Law constant = 1.73X10-8 atm cu-m/mol at 25 °C |
| Stability/Shelf Life |
Mixtures of glycerin with water, ethanol (95%), and propylene glycol are chemically stable. Glycerin may crystallize if stored at low temperatures; the crystals do not melt until warmed to 20 °C. |
| Autoignition Temperature |
698 °F (USCG, 1999) |
| Decomposition |
Pure gycerin is not prone to oxidation by the atmosphere under ordinary conditions, but is decomposes on heating with the evolution of toxic acrolein. |
| Viscosity |
954 CENTIPOISES AT 25 °C; 17 CENTIPOISES AT 25 °C (70% SOLN) |
| Heat of Combustion |
-4310 cal/g |
| Heat of Vaporization |
160 cal/g |
| pH |
Neutral to litmus |
| Refractive Index |
[n]D/20 between 1,471 and 1,474 |
| Dissociation Constants |
pKa = 14.4 |
| Kovats Retention Index |
2322 2314 2301.1 2300 2302.6 |
| Other Experimental Properties |
Solidifies after prolonged cooling at 0 °C forming shiny orthorhombic crystals |
| Chemical Classes |
Other Classes -> Alcohols and Polyols, Other |