CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Solid |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 238-242 °C |
| Solubility | 1.68e-01 g/L |
| LogP | 2.9 |
| Optical Rotation | Specific optical rotation: -193 °C at 25 °C/D |
| Decomposition | When heated to decomposition material emits toxic fumes of /nitrogen oxides, hydrogen fluoride, hydrogen chloride/. /Moxifloxacin hydrochloride/ |
| Dissociation Constants | 9.14 |
| Collision Cross Section | 198.5 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: TW, Method: calibrated with Waters Major Mix] |
| Other Experimental Properties | Slightly yellow to yellow crystalline powder, mp 324-325 °C (decomposes), specific optical rotation: -256 °C at 25 °C/D (c = 0.5 in water) /Moxifloxacin hydrochloride/ |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 401.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 0.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 401.17508442 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 401.17508442 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 82.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 29 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 727 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
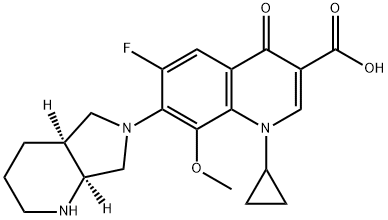
Moxifloxacin is a quinolone that consists of 4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid bearing a cyclopropyl substituent at position 1, a fluoro substitiuent at position 6, a (4aS,7aS)-octahydro-6H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridin-6-yl group at position 7 and a methoxy substituent at position 8. A member of the fluoroquinolone class of antibacterial agents. It has a role as an antibacterial drug. It is a quinolinemonocarboxylic acid, a quinolone, a member of cyclopropanes, a pyrrolidinopiperidine, an aromatic ether, a quinolone antibiotic and a fluoroquinolone antibiotic. It is a conjugate base of a moxifloxacinium(1+).