CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Solid |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | White to practically white fine powder |
| Boiling Point | 83-88 |
| Melting Point | 116-117 °C |
| Solubility | soluble in ethanol, DMSO, and dimethyl formamide at 30 mg/mL |
| LogP | 1.499 |
| Stability/Shelf Life | Stable under recommended storage conditions. |
| Decomposition | Hazardous decomposition products formed under fire conditions. - Carbon oxides, nitrogen oxides (NOx). |
| Dissociation Constants | 4.73 |
| Collision Cross Section | 202 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: TW, Method: calibrated with polyalanine and drug standards] |
| Other Experimental Properties | White or practically white crystalline powder. Practically odorless. Slightly soluble in water, freely soluble in sodium hydroxide solution, in n-butylamine, and in dimethylformamide; sparingly soluble in methanol; insoluble in ether, in chloroform, and in dilute mineral acids. /Hydrochlorothiazide/ |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 435.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 4.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 10 |
| Exact Mass | 435.22703980 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 435.22703980 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 112 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 32 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 608 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
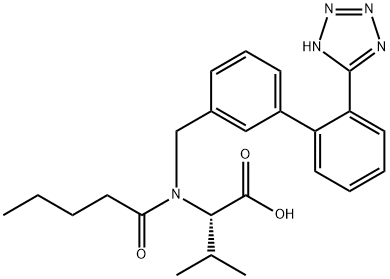
Valsartan is a monocarboxylic acid amide consisting of L-valine in which the amino hydrogens have been replaced by a pentanoyl and a [2'-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl group. It exhibits antihypertensive activity. It has a role as an antihypertensive agent, an angiotensin receptor antagonist, a xenobiotic and an environmental contaminant. It is a biphenylyltetrazole, a monocarboxylic acid amide and a monocarboxylic acid.