CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Solid |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | Prismatic needles from acetone, ethanol+ether or methanol+ethyl acetate |
| Melting Point | 153.5 °C |
| Solubility | Soluble in ethanol, ethyl ether, acetone, DMSO; slightly soluble in benzene |
| LogP | -0.64 |
| Dissociation Constants | pKa = 7.66 (approx., at 25 °C) |
| Collision Cross Section | 121.9 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: TW, Method: calibrated with polyalanine and drug standards] |
| Kovats Retention Index | 1192.1 1220.3 |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 142.11 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | -0.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 142.02660867 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 142.02660867 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 66.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 10 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 214 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
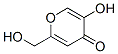
Kojic acid is a pyranone that is 4H-pyran substituted by a hydroxy group at position 5, a hydroxymethyl group at position 2 and an oxo group at position 4. It has been isolated from the fungus Aspergillus oryzae. It has a role as a NF-kappaB inhibitor, an Aspergillus metabolite, a skin lightening agent, an EC 1.10.3.1 (catechol oxidase) inhibitor, an EC 1.10.3.2 (laccase) inhibitor, an EC 1.13.11.24 (quercetin 2,3-dioxygenase) inhibitor, an EC 1.14.18.1 (tyrosinase) inhibitor and an EC 1.4.3.3 (D-amino-acid oxidase) inhibitor. It is an enol, a primary alcohol and a member of 4-pyranones. It derives from a hydride of a 4H-pyran.