CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Solid |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 176 °C |
| Solubility | 1000000 mg/L |
| LogP | -5.5 |
| Collision Cross Section | 196.4 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: DT, Method: single field calibrated with Agilent tune mix (Agilent)] |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 507.18 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | -5.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 17 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Exact Mass | 506.99574658 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 506.99574658 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 279 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 31 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 800 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
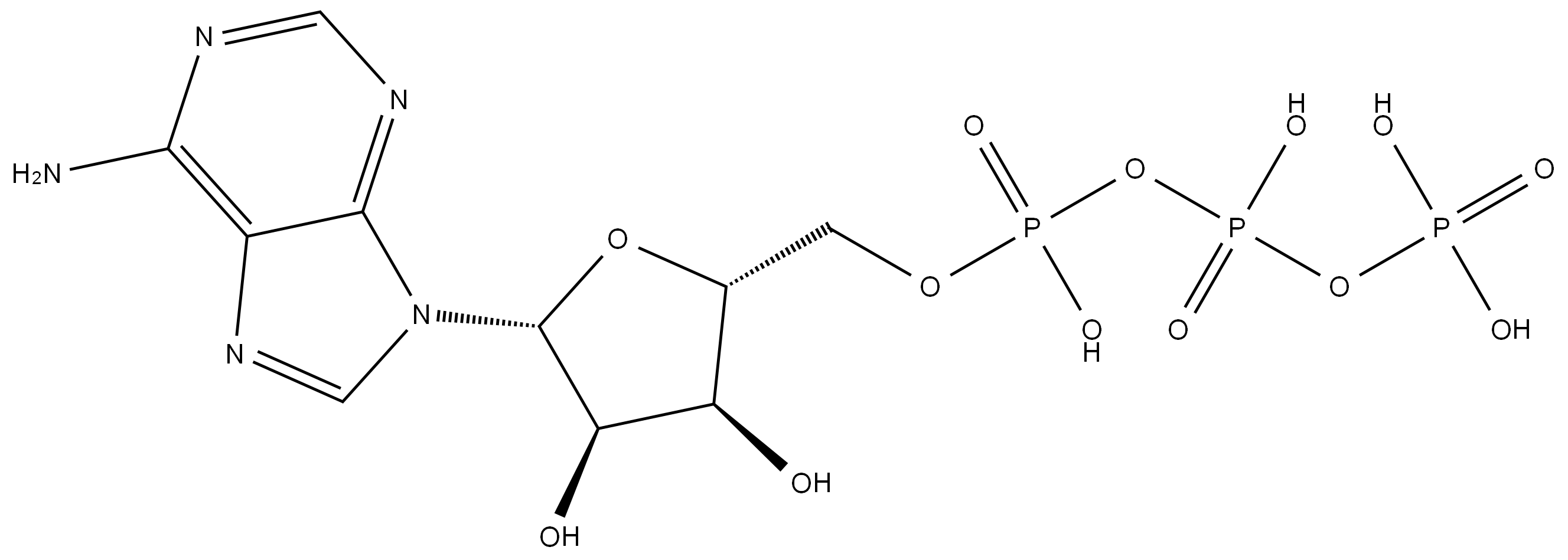
ATP is an adenosine 5'-phosphate in which the 5'-phosphate is a triphosphate group. It is involved in the transportation of chemical energy during metabolic pathways. It has a role as a nutraceutical, a micronutrient, a fundamental metabolite and a cofactor. It is an adenosine 5'-phosphate and a purine ribonucleoside 5'-triphosphate. It is a conjugate acid of an ATP(3-).