CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Solid |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 240.5-241.5 |
| Solubility | Slightly soluble |
| LogP | -0.3 |
| Dissociation Constants | 8.7 |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 229.63 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | -0.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 229.0478856 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 229.0478856 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 159 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 15 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 279 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
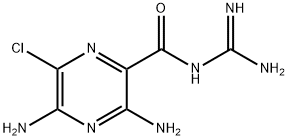
Amiloride is a member of the class of pyrazines resulting from the formal monoacylation of guanidine with the carboxy group of 3,5-diamino-6-chloropyrazine-2-carboxylic acid. It has a role as a sodium channel blocker and a diuretic. It is a member of pyrazines, an organochlorine compound, an aromatic amine and a member of guanidines. It is a conjugate base of an amiloride(1+).